Comparing Off-Grid Power Generation: Biogas Systems vs. Solar Systems
Off-grid power generation is a critical consideration for those seeking self-sufficiency and sustainable living. Two popular options are biogas systems and solar systems, each with its own advantages and cost implications. In this article, we’ll delve into the possibilities of cost savings, initial and long-term costs, and explore the comparative benefits of these systems for off-grid power generation.
Biogas Systems: Harnessing Energy from Waste
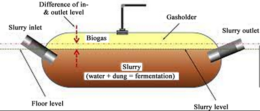
Biogas systems utilize organic waste, such as food scraps, agricultural residues, and animal manure, to produce biogas—a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide. This gas can be used for cooking, heating, and electricity generation through a biogas generator.
Initial Costs:
- Biogas Digester: The initial investment includes the cost of constructing a biogas digester, which can vary based on size and design complexity.
- Biogas Generator: A generator capable of utilizing biogas to produce electricity is required, adding to the initial cost.
- Storage and Distribution: Infrastructure for storing and distributing biogas needs to be set up, impacting the overall cost.
Long-Term Benefits:
- Cost Savings: Biogas systems capitalize on organic waste, reducing disposal costs and offering an ongoing supply of biogas.
- Energy Reliability: Biogas can be produced consistently as long as organic waste is available, providing a reliable source of energy.
Solar Systems: Tapping into Solar Energy
Solar systems capture sunlight using photovoltaic (PV) panels to convert it into electricity. These systems can be supplemented with battery backup to store excess energy for use during periods of low sunlight.
Initial Costs:
- Solar Panels: The cost of solar panels depends on their capacity and efficiency, which can influence the initial investment.
- Inverter: An inverter is needed to convert the DC power generated by solar panels into AC power for use.
- Battery Storage (Optional): If a battery backup is desired for continuous power supply, it involves additional upfront costs.
Long-Term Benefits:
- Low Operating Costs: Solar systems have minimal operating and maintenance costs once installed.
- Sustainable Energy Source: Solar energy is renewable and abundant, offering a clean and eco-friendly power solution.
Comparing the Costs:
Biogas Systems:
- Initial costs can be relatively higher for a complex system and inversely lower for a very basic horizontal system.
- Cost savings over time can be substantial if organic waste is readily available.
- Long-term maintenance and repair costs may vary based on system complexity.
Solar Systems:
- Initial costs can vary with battery storage and complexity.
- Minimal ongoing maintenance expenses.
- Battery backup increases the initial investment but may provides continuous power during cloudy periods if sized properl.
Considerations for Off-Grid Homesteads:
- Resource Availability: Biogas systems require a consistent supply of organic waste, while solar systems depend on sunlight availability.
- Environmental Impact: Biogas systems help manage organic waste and reduce methane emissions, while solar systems offer a carbon-neutral energy source.
- Energy Demand: Assess your power requirements to determine the suitable system size and battery backup capacity.
Conclusion:
The choice between biogas systems and solar systems for off-grid power generation involves careful consideration of initial costs, long-term benefits, and resource availability. Biogas systems capitalize on organic waste to provide consistent energy, while solar systems harness renewable sunlight. The decision ultimately depends on the unique needs and priorities of your off-grid homestead, aiming for a balance between cost-effectiveness and sustainability. Bio-gas can also provide uninterrupted power during long cloudy and periods of bad weather.
